A new class of cloud provider, the "neocloud," has emerged to service the voracious computational demands of the artificial intelligence (AI) revolution.1 Unlike traditional hyperscalers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, which offer a vast "supermarket" of general-purpose services, neoclouds are highly specialized "delicatessens".2 Their singular focus is delivering GPU-as-a-Service (GPUaaS) with maximum performance, flexibility, and cost-efficiency for AI and High-Performance Computing (HPC) workloads.2 Providers like CoreWeave, Lambda Labs, and Crusoe Energy have built their businesses on this purpose-built model, stripping away extraneous services to concentrate on providing raw, scalable GPU power.2
This GPU-centric paradigm, however, introduces a critical shift in infrastructure dynamics. As computational power becomes abundant, the primary performance bottleneck moves from the processor to the data pipeline. The storage subsystem is no longer a passive repository but an active, performance-critical component of the AI factory. Its architecture directly dictates GPU utilization, job completion times, and, ultimately, the economic viability of the entire neocloud model.1 An underperforming storage layer leads to idle, multi-million-dollar GPU clusters, negating the very value proposition of the neocloud.7
The business model of neoclouds inverts traditional infrastructure pressures. Hyperscalers typically build vast, general-purpose infrastructure and then seek workloads to fill it. In contrast, neoclouds often acquire highly sought-after GPU resources first and then must construct the most efficient infrastructure around them to maximize their return on investment. This inversion places intense pressure on every other component, especially storage and networking, to be a pure performance enabler rather than a source of latency or a cost center.8 The success of a neocloud hinges on its ability to deliver predictable, peak performance in a demanding, multi-tenant environment—a challenge that falls squarely on the storage architecture.1 This economic reality is the primary force driving the adoption of advanced, parallel storage platforms over traditional enterprise Network Attached Storage (NAS).

Section 1: The Neocloud Storage Blueprint
Evaluating storage for the unique demands of neoclouds requires a sophisticated framework that distinguishes between foundational necessities and strategic, performance-defining differentiators. This blueprint moves beyond a simple feature checklist to define the architectural principles that underpin a truly AI-ready data platform.
Table Stakes: The Foundational Requirements
These are the non-negotiable capabilities that any storage platform must possess to be considered viable for a modern neocloud environment.
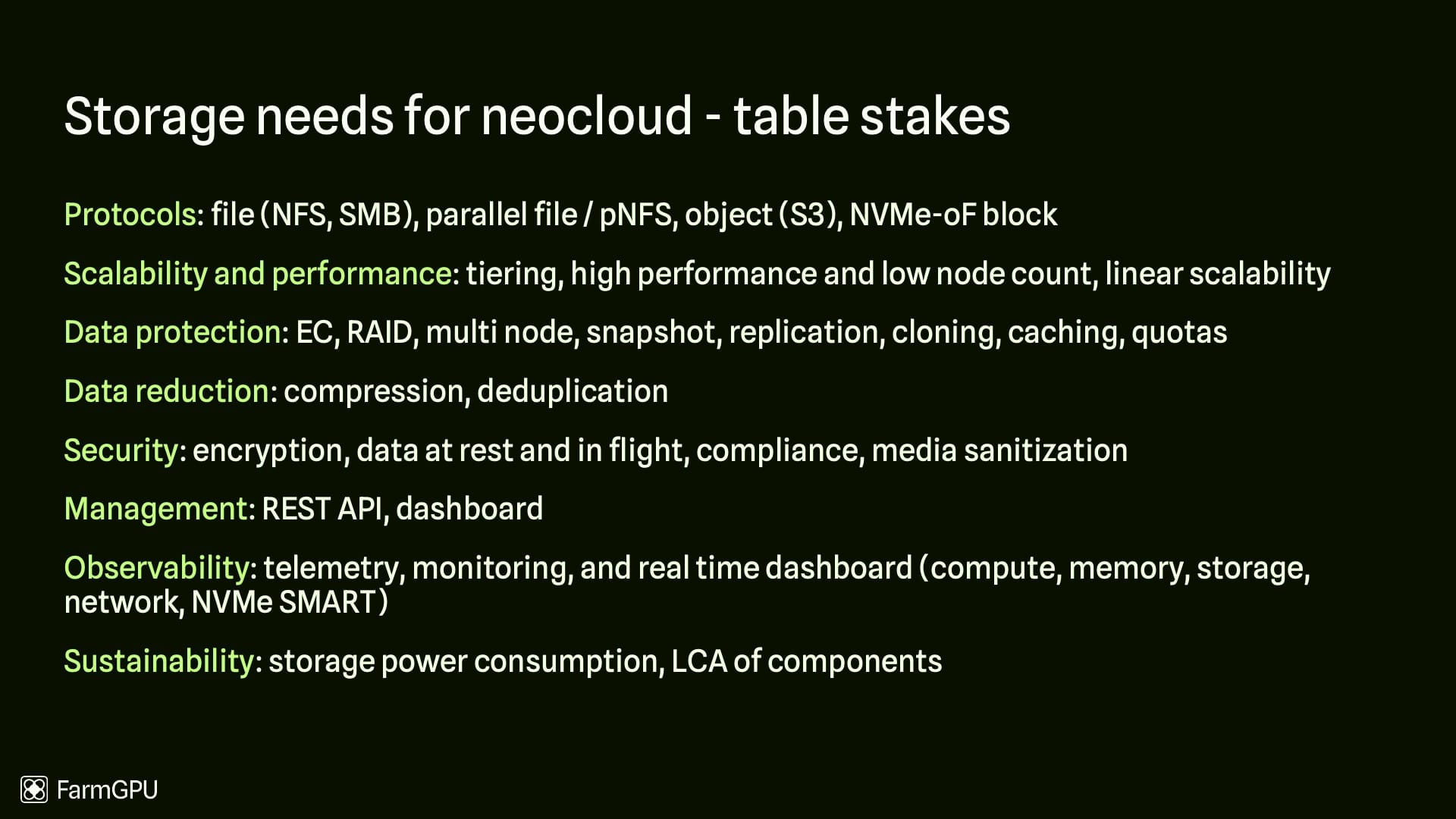
- Versatile Protocol Support: AI pipelines are heterogeneous, requiring a unified storage platform that speaks multiple languages without performance trade-offs. This includes file protocols like Network File System (NFS) and Server Message Block (SMB) for traditional Linux and Windows-based development, high-performance parallel file systems (including pNFS), the ubiquitous Amazon S3 API for cloud-native applications, and low-latency block protocols like NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) for the most demanding transactional workloads.9
- Scalability and Performance: The architecture must deliver extreme performance to prevent I/O stall, where expensive GPUs wait for data.11 This means providing both high throughput for large sequential reads (e.g., model loading) and high IOPS for metadata-heavy or small-file workloads.12 Performance must scale linearly as the cluster grows, and the system should support intelligent tiering to balance cost and speed, automatically moving data between hot and cold tiers.13
- Comprehensive Data Protection: At petabyte and exabyte scale, traditional RAID is insufficient due to long rebuild times.15 Modern scale-out erasure coding is the standard, offering superior data durability and faster, parallelized rebuilds.17 This must be complemented by enterprise data services like space-efficient snapshots for recovery points, zero-copy clones for rapid dev/test environments, caching to accelerate access, and quotas to manage multi-tenant resources.18
- Efficient Data Reduction: To make all-flash storage economically viable at scale, advanced data reduction is essential. This includes both compression, which shrinks data size algorithmically, and deduplication, which eliminates redundant data blocks by replacing them with pointers.21 These techniques significantly reduce the physical storage footprint and associated costs.23
- Robust Security: In a multi-tenant neocloud environment, security is paramount. The platform must provide end-to-end encryption for data-at-rest (on disk) and data-in-flight (across the network).24 It must also support regulatory compliance standards and offer secure media sanitization methods to permanently erase data from retired hardware.27
- Modern Management and Observability: Neoclouds require automation and deep insight into their infrastructure. A comprehensive REST API is crucial for programmatic management and integration into orchestration workflows.30 This must be paired with robust observability, including real-time dashboards and telemetry for monitoring the health and performance of compute, memory, storage, and network resources, down to NVMe SMART attributes.32
- Focus on Sustainability: As AI clusters consume vast amounts of power, sustainability has become a critical design consideration. This includes measuring and minimizing the storage system's power consumption and considering the complete lifecycle assessment (LCA) of its components.35
Best-in-Class: The Strategic Differentiators
These are the advanced capabilities that separate leading AI storage platforms from the rest, enabling maximum performance, efficiency, and future-readiness.

- Hardware Acceleration and Offload: The most advanced platforms leverage hardware to offload tasks from the host CPU. This includes support for Data Processing Units (DPUs) like NVIDIA's BlueField, which can accelerate networking, security, and storage services.37 Critically, this also means native support for NVIDIA GPUDirect Storage, a technology that creates a direct data path between storage and GPU memory, bypassing the CPU to dramatically reduce latency and increase throughput.40
- AI-Specific Workload Optimization: Leading platforms are optimized for emerging AI workloads. This includes native support for vector databases essential for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and the ability to use SSDs as an extension of GPU memory (SSD offload) for training massive models.43
- High-Performance Object and Parallel File Systems: A best-in-class solution must offer a high-performance object store with a native S3 endpoint, as S3 has become the de facto standard for AI data lakes.47 This must be complemented by a high-bandwidth parallel file system architected to handle the extreme, concurrent write patterns of large-scale model checkpointing without impacting training performance.49
- Inference and Memory Optimization: As inference becomes a dominant workload, storage must actively participate in optimizing it. This includes support for offloading the Key-Value (KV) Cache—which can consume enormous amounts of GPU memory—to high-speed storage.51 Integration with frameworks like NVIDIA Dynamo and libraries like vLLM is a key indicator of a platform's readiness for next-generation inference.53
- Advanced Security and Manageability: Beyond standard encryption, leading solutions are adopting confidential computing, which uses hardware-based Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) to protect data even while it's being processed in memory.56 This is often anchored by a hardware root of trust for ultimate security.58 On the management front, deep integration with Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) tools provides a full inventory and holistic view of the data center.60
- Next-Generation Sustainability: Top-tier platforms go beyond basic power efficiency. They incorporate runtime power optimizations that dynamically adjust consumption based on workload.62 They also provide reporting for Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions and are designed with circularity and reusability in mind, minimizing e-waste and promoting a more sustainable hardware lifecycle.64
Section 2: The Titans of AI Storage: NVIDIA NCP Partners Checking the Boxes
The NVIDIA Cloud Partner (NCP) program includes a select group of storage vendors whose solutions have been validated to meet the stringent performance and scalability demands of AI infrastructure. These partners are actively delivering on the table stakes and best-in-class features required by neoclouds.
- VAST Data has pioneered the Disaggregated and Shared-Everything (DASE) architecture, which decouples compute logic from physical storage media.67 This allows for independent scaling of performance and capacity, a key neocloud requirement. VAST's platform is designed to make all-flash storage economical at scale by using cost-effective QLC flash and advanced data reduction, and it is certified for NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD with full support for GPUDirect Storage.68
- WEKA offers a software-defined platform built on WekaFS, a high-performance parallel filesystem designed for extreme low latency. Its unique architecture runs in user space, bypassing the host kernel to reduce I/O overhead, making it ideal for small-file and metadata-intensive workloads.70 As an early adopter of GPUDirect Storage, WEKA is deeply integrated with the NVIDIA ecosystem, including emerging technologies like the NVIDIA Dynamo inference framework.42
- DDN brings decades of experience from the world's largest supercomputing environments with its A³I (Accelerated, Any-Scale AI) solutions, built on the hardened EXAScaler/Lustre parallel filesystem.72 Battle-tested in massive deployments like NVIDIA's own Eos supercomputer, DDN's architecture excels at large-scale training throughput, offering features like "Hot Nodes" client-side caching to optimize the I/O patterns of distributed deep learning jobs.72
- The Broader Ecosystem of NVIDIA-certified partners provides mature, feature-rich alternatives. Pure Storage offers its FlashBlade//S platform, emphasizing operational simplicity and power efficiency within ubiquitous Ethernet environments.74NetApp brings its mature ONTAP operating system to the AI era, focusing on integrating its intelligent data infrastructure to power advanced RAG and agentic AI workflows.75IBM contributes its Storage Scale (formerly GPFS), another veteran parallel filesystem with deep roots in HPC, providing a unified platform for file and object data.77 This rich ecosystem, which also includes Dell, HPE, and others, gives neocloud builders a wide array of validated choices.79
| Feature | VAST Data | WEKA | DDN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Architecture | Disaggregated & Shared-Everything (DASE) | Software-Defined Parallel Filesystem (WekaFS) | Shared Parallel Filesystem (EXAScaler/Lustre) |
| Primary Media | QLC Flash + Storage Class Memory (SCM) | All-NVMe Flash | All-NVMe Flash |
| Filesystem Type | Global, Log-Structured | Distributed, Parallel | Parallel |
| Key Differentiator | Economics of All-Flash at Exabyte Scale | Extreme Low-Latency via User-Space I/O | Proven HPC-Scale Throughput & Caching |
| GPU Integration | GDS, DGX SuperPOD Certified | GDS, DGX SuperPOD Certified, Dynamo/NIXL | GDS, DGX SuperPOD Certified |
| Small File Handling | Similarity-Based Global Data Reduction | Fully Distributed Metadata | Lustre Optimizations |
| Caching Strategy | All-Flash (No Caching Tier) | Tiering to S3 Object Storage | "Hot Nodes" Client-Side Caching |
| Deployment Model | Hardware Appliance | Software-Defined / Hardware Appliance | Hardware Appliance |
Section 3: Future Frontiers: Data Orchestration and Storage-Aware AI
While today's leaders deliver immense performance, emerging players are tackling the next major challenge: managing data across a globally distributed landscape and integrating storage even more deeply into the AI compute fabric.
Solving Data Gravity with Global Orchestration
As AI workloads become more distributed, the physical location of data creates "data gravity"—the difficulty of moving massive datasets to compute resources. Emerging players like Hammerspace are addressing this with a software-defined Global Data Environment. Hammerspace creates a single, unified global namespace across existing, heterogeneous storage systems.80 It leverages Parallel NFS (pNFS), a standards-based protocol built into the Linux kernel, to separate metadata from the data path. This allows Hammerspace to act as an intelligent data orchestration layer, using policies to automatically move data between storage tiers and locations in the background, making data appear local to applications wherever they run.80
Another emerging player, PEAK:AIO, is carving out a niche by focusing on the mid-scale AI cluster, where traditional enterprise storage can be overly complex and expensive.83 PEAK:AIO's software-defined approach transforms standard server hardware into a high-performance "AI Data Server," designed from the ground up for the specific needs of AI workloads.85 The architecture prioritizes simplicity and cost-effectiveness, maintaining the ease of use of standard NFS while turbo-charging it with RDMA and GPUDirect support to deliver ultra-low latency and high bandwidth directly to GPUs.83 This allows organizations to start small and scale linearly without over-investing in storage, freeing up budget for critical GPU resources.84 Looking ahead, PEAK:AIO is also addressing next-generation challenges with its "Token Memory Architecture," a dedicated appliance designed to unify KVCache acceleration and GPU memory expansion using CXL memory, treating token history as a memory tier rather than a storage problem.88
The Next Frontier: Storage-Aware AI and Infrastructure Offload
The evolution of AI is blurring the lines between storage, memory, and compute, creating a new paradigm of "storage-aware" AI. Techniques like Microsoft's ZeRO-Infinity offload model parameters and optimizer states to fast NVMe SSDs, using them as an extended memory tier.43 In LLM inference, the Key-Value (KV) Cache is a major consumer of precious GPU VRAM; emerging solutions like vLLM and NVIDIA's Dynamo inference server can intelligently offload portions of this cache to high-speed networked storage.51 This creates a new, extremely latency-sensitive workload where the storage system must serve cache blocks with memory-like speed. This future is enabled by DPUs, which are designed to manage these complex data movements efficiently, fetching data from networked storage and placing it directly into GPU memory via GDS without involving the host CPU.82 This fundamental shift elevates the importance of ultra-low-latency, parallel storage from a "performance optimization" to an "enabling technology" for the next generation of AI.
Conclusion: Architecting for Intelligence
The rise of the neocloud signifies a fundamental shift in computing infrastructure, one purpose-built for the age of AI. This analysis demonstrates that while GPUs provide the raw computational force, the storage platform is the critical subsystem that governs the efficiency, scalability, and ultimate profitability of a neocloud's AI factory. Choosing the right storage is not a matter of selecting the "fastest" option on a spec sheet, but of selecting the platform with the right architecture for the unique and demanding workloads of AI.
The blueprint for a best-in-class neocloud storage solution is clear. It begins with a foundation of "table stakes" features—from multi-protocol support and linear scalability to robust data protection and security. Upon this foundation, "best-in-class" differentiators are built: deep hardware integration with technologies like GPUDirect Storage and DPUs, specific optimizations for emerging workloads like RAG and KV Cache offload, and a forward-looking approach to security and sustainability.
Looking forward, the line between storage and memory will continue to blur. The most successful neoclouds will be those that embrace this paradigm, building their infrastructure not on siloed resources, but on an integrated, intelligent data platform where storage actively participates in the entire AI lifecycle. The choice of storage architecture is therefore one of the most critical strategic decisions a neocloud provider can make, a decision that will fundamentally define its performance, its capabilities, and its position in the competitive landscape of AI infrastructure.
Works cited
- Understanding Neocloud offering GPU-as-a-Service (GPUaaS) - DriveNets, accessed August 17, 2025, https://drivenets.com/resources/education-center/what-are-neocloud-providers/
- What is a Neocloud? - NEXTDC, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.nextdc.com/blog/what-is-a-neo-cloud
- NeoClouds: The Next Generation of AI Infrastructure - Voltage Park, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.voltagepark.com/blog/neoclouds-the-next-generation-of-ai-infrastructure
- Neocloud Providers: Powering the Next Generation of AI Workloads - Rafay, accessed August 17, 2025, https://rafay.co/ai-and-cloud-native-blog/neocloud-providers-next-generation-ai-workloads/
- What Are Neoclouds and Why Does AI Need Them? - RTInsights, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.rtinsights.com/what-are-neoclouds-and-why-does-ai-need-them/
- Why Storage Is the Unsung Hero for AI, accessed August 17, 2025, https://blog.purestorage.com/perspectives/why-storage-is-the-unsung-hero-for-ai/
- DDN: Data Intelligence Platform Built for AI, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.ddn.com/
- How to Build an AI-Ready Infrastructure, like a Neocloud - NEXTDC, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.nextdc.com/blog/how-to-build-like-a-neo-cloud
- NFS vs SMB - Difference Between File Access Storage Protocols - AWS, accessed August 17, 2025, https://aws.amazon.com/compare/the-difference-between-nfs-smb/
- Virtual Machine Storage – File vs Block [Part 1]: SMB & NFS vs iSCSI & NVMe-oF - StarWind, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.starwindsoftware.com/blog/virtual-machine-storage-file-vs-block-part-1/
- Unsung hero of AI World: Storage - Medium, accessed August 17, 2025, https://medium.com/@lazygeek78/unsung-hero-of-ai-world-storage-7cb5f342db81
- Optimizing AI: Meeting Unstructured Storage Demands Efficiently, accessed August 17, 2025, https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/sv-se/p/optimizing-ai-meeting-unstructured-storage-demands-efficiently/
- Why Auto-Tiering is Essential for AI Solutions: Optimizing Data Storage from Training to Long-Term Archiving - insideAI News, accessed August 17, 2025, https://insideainews.com/2024/11/11/why-auto-tiering-is-essential-for-ai-solutions-optimizing-data-storage-from-training-to-long-term-archiving/
- On-prem, cloud, or hybrid? Choosing the right storage strategy for AI workloads - Wasabi, accessed August 17, 2025, https://wasabi.com/blog/industry/storage-strategy-for-ai-workloads
- Understanding Erasure Coding And Its Difference With RAID - StoneFly, Inc., accessed August 17, 2025, https://stonefly.com/blog/understanding-erasure-coding/
- What is erasure coding and how does it differ from RAID? : r/DataHoarder - Reddit, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.reddit.com/r/DataHoarder/comments/630zd6/what_is_erasure_coding_and_how_does_it_differ/
- What is Erasure Coding? - Supermicro, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.supermicro.com/en/glossary/erasure-coding
- Snapshot vs Clone in Storage - Simplyblock, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.simplyblock.io/glossary/snapshot-vs-clone-in-storage/
- Snapshots or Clones for Data Protection? - Verge.io, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.verge.io/blog/storage/snapshots-or-clones-for-data-protection/
- Manage and increase quotas for resources - Azure AI Foundry - Microsoft Learn, accessed August 17, 2025, https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-foundry/how-to/quota
- Data deduplication vs. data compression - Lytics CDP, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.lytics.com/blog/data-deduplication-vs-data-compression/
- Effective Deduplication & Compression - DataCore Software, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.datacore.com/products/sansymphony/deduplication-compression/
- Deduplication, data compression, data compaction, and storage efficiency - NetApp, accessed August 17, 2025, https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap/volumes/deduplication-data-compression-efficiency-concept.html
- Storage Encryption & Disk Encryption – Cyber Resilience | NetApp, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.netapp.com/cyber-resilience/storage-encryption/
- Encryption in transit for Google Cloud | Security, accessed August 17, 2025, https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/encryption-in-transit
- Azure Data Encryption-at-Rest - Microsoft Learn, accessed August 17, 2025, https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/security/fundamentals/encryption-atrest
- Media sanitization guidelines | Internal Revenue Service, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.irs.gov/privacy-disclosure/media-sanitization-guidelines
- What is Media Sanitization - ITAD Services Company TechReset, accessed August 17, 2025, https://techreset.com/itad-guides/what-is-media-sanitization/
- www.irs.gov, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.irs.gov/privacy-disclosure/media-sanitization-guidelines#:~:text=Destruction%20of%20media%20is%20the,%2C%20pulverizing%2C%20shredding%20and%20melting.
- Azure Storage REST API Reference - Microsoft Learn, accessed August 17, 2025, https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/rest/api/storageservices/
- Using Apigee API management for AI | Google Cloud Blog, accessed August 17, 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/api-management/using-apigee-api-management-for-ai
- What is AI observability? - Dynatrace, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.dynatrace.com/knowledge-base/ai-observability/
- SMART + NVMe status | Grafana Labs, accessed August 17, 2025, https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/16514-smart-nvme-status/
- How to Check & Monitor NVMe SSD Drive Health, accessed August 17, 2025, https://ulink-da.com/how-to-check-nvme-drive-health/
- Checkpointing in AI workloads: A primer for trustworthy AI. - Seagate Technology, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.seagate.com/blog/checkpointing-in-ai-workload-a-primer-for-trustworthy-ai/
- Simplify Enterprise AI with Pure and NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD - Pure Storage Blog, accessed August 17, 2025, https://blog.purestorage.com/products/simplify-enterprise-ai-with-certified-pure-storage-and-nvidia-dgx-superpod/
- A data-processing unit, or DPU, is a type of specialized processor that's designed to offload and accelerate the networking, storage, and security workloads that would traditionally be handled by the CPU in a server. The idea is to free up the CPU so that it can focus more on running applications and processing data specific to the user's tasks. - ASUS Servers, accessed August 17, 2025, https://servers.asus.com/glossary/DPU
- NVIDIA Bluefield Data Processing Unit | DPU - ASBIS solutions, accessed August 17, 2025, https://solutions.asbis.com/products/storage/bluefield-data-processing-units-dpu-
- NVIDIA BlueField Networking Platform, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/networking/products/data-processing-unit/
- 1. Overview Guide — GPUDirect Storage Overview Guide - NVIDIA Docs Hub, accessed August 17, 2025, https://docs.nvidia.com/gpudirect-storage/overview-guide/index.html
- NVIDIA GPUDirect Storage: 4 Key Features, Ecosystem & Use Cases - Cloudian, accessed August 17, 2025, https://cloudian.com/guides/data-security/nvidia-gpudirect-storage-4-key-features-ecosystem-use-cases/
- What is GPUDirect Storage? | WEKA, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.weka.io/learn/glossary/gpu/what-is-gpudirect-storage/
- MemAscend: System Memory Optimization for SSD-Offloaded LLM Fine-Tuning - arXiv, accessed August 17, 2025, https://arxiv.org/html/2505.23254v1
- AI TOP 100E SSD 2TB Key Features | SSD - GIGABYTE Global, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.gigabyte.com/SSD/AI100E2TB
- milvus.io, accessed August 17, 2025, https://milvus.io/ai-quick-reference/what-are-the-hardware-requirements-for-hosting-a-legal-vector-db#:~:text=Storage%20and%20networking%20are%20equally,on%20vector%20dimensions%20and%20metadata.
- What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)? - Google Cloud, accessed August 17, 2025, https://cloud.google.com/use-cases/retrieval-augmented-generation
- AI Storage is Object Storage - MinIO, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.min.io/solutions/object-storage-for-ai
- MinIO is a high-performance, S3 compatible object store, open sourced under GNU AGPLv3 license. - GitHub, accessed August 17, 2025, https://github.com/minio/minio
- Parallel file systems for HPC workloads | Cloud Architecture Center, accessed August 17, 2025, https://cloud.google.com/architecture/parallel-file-systems-for-hpc
- Announcing the MLPerf Storage v2.0 Checkpointing Workload - MLCommons, accessed August 17, 2025, https://mlcommons.org/2025/08/storage-2-checkpointing/
- SpeCache: Speculative Key-Value Caching for Efficient Generation of LLMs - arXiv, accessed August 17, 2025, https://arxiv.org/html/2503.16163v1
- KV cache strategies - Hugging Face, accessed August 17, 2025, https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/kv_cache
- Accelerate generative AI inference with NVIDIA Dynamo and Amazon EKS - AWS, accessed August 17, 2025, https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/accelerate-generative-ai-inference-with-nvidia-dynamo-and-amazon-eks/
- What is vLLM? - Red Hat, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/ai/what-is-vllm
- Dynamo Inference Framework - NVIDIA Developer, accessed August 17, 2025, https://developer.nvidia.com/dynamo
- What Is Confidential Computing? Defined and Explained - Fortinet, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/confidential-computing
- Confidential computing - Wikipedia, accessed August 17, 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Confidential_computing
- Hardware Root of Trust: Everything you need to know - Rambus, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.rambus.com/blogs/hardware-root-of-trust/
- FAQs: What is Root of Trust? - Thales CPL, accessed August 17, 2025, https://cpl.thalesgroup.com/faq/hardware-security-modules/what-root-trust
- Best Data Center Infrastructure Management Tools Reviews 2025 | Gartner Peer Insights, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.gartner.com/reviews/market/data-center-infrastructure-management-tools
- What Is Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM)? - Pure Storage, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.purestorage.com/knowledge/what-is-data-center-infrastructure-management.html
- Delta Lake table optimization and V-Order - Microsoft Fabric, accessed August 17, 2025, https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/data-engineering/delta-optimization-and-v-order
- Power Allocation and Capacity Optimization Configuration of Hybrid Energy Storage Systems in Microgrids Using RW-GWO-VMD - MDPI, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/18/16/4215
- Scope 1, 2, and 3 Emissions Explained | CarbonNeutral, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.carbonneutral.com/news/scope-1-2-3-emissions-explained
- What Are Scope 1, 2 and 3 Emissions? - IBM, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/scope-1-2-3-emissions
- Hardware harvesting at Google: Reducing waste and emissions | Google Cloud Blog, accessed August 17, 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/sustainability/hardware-harvesting-at-google-reducing-waste-and-emissions
- DASE (Disaggregated and Shared Everything) | Continuum Labs, accessed August 17, 2025, https://training.continuumlabs.ai/infrastructure/vast-data-platform/dase-disaggregated-and-shared-everything
- VAST Data Achieves NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD Certification | Inside HPC & AI News, accessed August 17, 2025, https://insidehpc.com/2023/05/vast-data-achieves-nvidia-dgx-superpod-certification/
- ACCELERATING A.I. WORKLOADS AT LIGHTSPEED - Military Expos, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.militaryexpos.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/VAST-Data_NVIDIA_GPU-Reference-Architecture.pdf
- WEKA Architecture Key Concepts, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.weka.io/wp-content/uploads/files/resources/WEKA-Architecture-Key-Concepts.pdf
- WEKA Accelerates AI Inference with NVIDIA Dynamo and NVIDIA NIXL, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.weka.io/blog/ai-ml/weka-accelerates-ai-inference-with-nvidia-dynamo-and-nvidia-nixl/
- Fully-validated and optimized AI High-Performance Storage ... - DDN, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.ddn.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FINAL-DDN-NCP-RA-20240626-A3I-X2-Turbo-WITH-NCP-1.1-GA-1.pdf
- NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD H100 - DDN, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.ddn.com/resources/reference-architectures/nvidia-dgx-superpod-h100/
- NVIDIA Technology Partnership - Pure Storage, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.purestorage.com/partners/technology-alliance-partners/nvidia.html
- NetApp Storage Now Validated for NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD, NVIDIA Cloud Partners, and NVIDIA-Certified Systems, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.netapp.com/newsroom/press-releases/news-rel-20250318-592455/
- Powering the next generation of enterprise AI infrastructure | NetApp Blog, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.netapp.com/blog/next-generation-enterprise-ai-infrastructure/
- NVIDIA AI storage solutions - IBM, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.ibm.com/solutions/storage/nvidia
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Storage Solutions - IBM, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.ibm.com/solutions/ai-storage
- Storage vendors rally behind Nvidia at GTC 2025 - Blocks and Files, accessed August 17, 2025, https://blocksandfiles.com/2025/03/18/nvidia-storage-announcements/
- Hammerspace - The Data Platform for AI Anywhere, accessed August 17, 2025, https://hammerspace.com/
- pNFS Provides Performance and New Possibilities - HPCwire, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.hpcwire.com/2024/02/29/pnfs-provides-performance-and-new-possibilities/
- DPUs Explained | How They Supercharge AI Infrastructure ⚙️ - YouTube, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Mek000MYik
- PEAK:AIO Storage - PNY Technologies, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.pny.com/en-eu/professional/software/peak-aio-storage
- AI Data Servers - Storage Reinvented - PEAK:AIO, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.peakaio.com/ai-data-servers/
- PEAK:AIO AI-controlled storage revolution - sysGen GmbH, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.sysgen.de/en/loesungen/data-storage/peak-aio/
- PEAKAIO About us, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.peakaio.com/about-us/
- PEAK:AIO, MONAI, and Solidigm: Revolutionizing Storage for Medical AI, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.solidigm.com/products/technology/peak-aio-monai-storage-for-medical-ai.html
- PEAK:AIO Introduces Token Memory Architecture to Address KVCache and GPU Bottlenecks - HPCwire, accessed August 17, 2025, https://www.hpcwire.com/off-the-wire/peakaio-introduces-token-memory-architecture-to-address-kvcache-and-gpu-bottlenecks/

